In recent years, there has been increasing talk of the extremely harmful effects that free radicals have on the human body. What is really behind these dangerous substances, which are attributed to dangerous diseases and even cancer?
In essence, free radicals are chemically unstable atoms, groups of atoms or molecules that contain one free electron each. Electrons, on the other hand, are negatively charged particles that have the property of forming chemical bonds with a very unstable base.
It is this instability that makes it possible to bind radicals to other compounds, turning them into new free radicals. This is a dangerous process, because once started, it develops rapidly and causes serious changes in the body, leading to numerous severe injuries.
Now is the time to say that in a normal state, free radicals are present in every person and most interestingly, they are there for a split second, but the damage they cause is dangerous and irreversible. According to some claims, every cell in our body produces thousands of free radicals every day.
Causes of free radical formation
So far it has become clear what free radicals are, but we need to raise the curtain on what causes them. Unfortunately, there are many factors that contribute to their formation and in the modern way of life they simply surround us everywhere - cigarette smoke, car gases, solar radiation and last but not least - the way we eat. Anyone who eats too much fat increases the activity of free radicals, because the conversion of fats into dangerous compounds is much easier than the conversion of proteins and carbohydrates.
Damage from free radicals
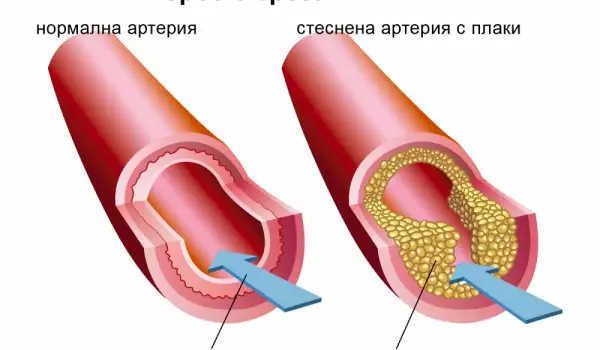
We have seen that free radicals are extremely harmful, but it is time to dwell in more detail on the damage they cause. They are responsible for the appearance of mutations affecting the cells and this makes them the direct culprit for processes such as hardening of the arterial walls (atherosclerosis), premature aging and the appearance of wrinkles, cataracts.
However, the most serious damage is the real possibility of some cancers. Free radicals can cause cardiovascular disease, diseases of the nervous system (Alzheimer's and Parkinson's), endocrine diseases (diabetes) and a number of pathological changes in the body.
And as in many other aspects, this has two sides as well. It turns out that free radicals can be useful, because white blood cells themselves produce free radicals to attack foreign cells when pathogens enter the body. This way, a process is formed in which the body neutralizes foreign cells and restores those affected.
Then why are free radicals so dangerous? The problem lies in the speed of development of the processes - when the formation of free radicals is extremely fast and with great speed there is an over-release of free radicals.
When the body is in a normal state, it manages to control their formation, because the cells produce both free radicals and antioxidants and they prevent changes this way. This means that everyone must prevent radical damage before it can happen. This is done with rational nutrition and healthy lifestyle, limiting stress and harmful effects to a minimum.
Antioxidants against free radicals
From everything written so far, it is clear that free radicals are dangerous compounds that can cause life-threatening diseases. That is why it is of utmost importance to know how to prevent their formation in order to enjoy a long life and good health. The key word here is antioxidants! These valuable substances for the body have the amazing ability to neutralize the action of free radicals, so we must consume them daily. But where do we get them and what are the best sources?
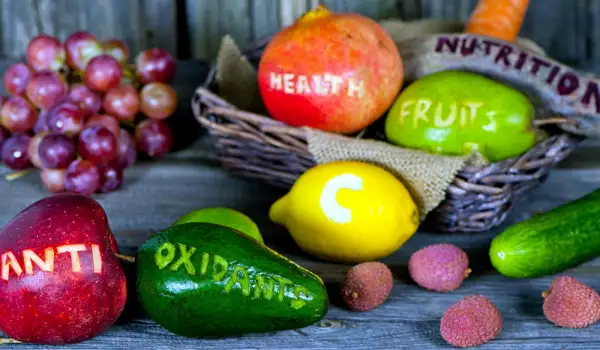
The highest antioxidant content can be found in fruit and vegetables, whole grains, legumes. The diet should be well balanced and rich in vitamins, minerals and fiber.
However, as with anything else, there are antioxidants that are more beneficial than others. Vitamin C is the most valuable antioxidant with a powerful anti-cancer effect. It is best in the fight against free radicals, so the recommended daily dose is between 100 and 250 mg.
Vitamin E is another important antioxidant that lowers blood pressure and strengthens the cardiovascular system. The daily requirement of vitamin E is between 30 and 80 mg. Beta-carotene is the third true fighter against free radicals. The daily intake should be 15 mg.
These three vitamins are found in citrus fruit, peppers, green leafy vegetables, eggs, carrots, tomatoes, peaches, nuts, fish, green tea, broccoli, potatoes. One of the most complete diets in the fight against free radicals is the Mediterranean, which with its richness of fresh fruit and vegetables, fish and olive oil is considered the most healthy in the world.
Dietary supplements are also recommended for the treatment of various diseases, but it should not be forgotten that sports and rational nutrition, cessation of alcohol and cigarettes are the best ways to adhere to a healthy lifestyle.


















Comments